Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
藤井 貴美夫
JAERI-Tech 2005-048, 108 Pages, 2005/09
天然ウランを燃料とする黒鉛減速炭酸ガス冷却型の日本原子力発電(株)東海発電所は、1998年3月31日に停止した。現在、同社において廃止措置に向けて検討が行われている。東海発電所や原研の高温工学試験研究炉の炉内には多くの黒鉛材料が使用されている。使用済み黒鉛を放射性廃棄物として考える場合、半減期が極めて長い炭素14( C)が含まれるため廃棄処理・処分する際に問題となることが予想される。
C)が含まれるため廃棄処理・処分する際に問題となることが予想される。 C濃度の問題を解決する一つの研究として、平成11年度から原研-原電共同研究で基礎データを取得した。
C濃度の問題を解決する一つの研究として、平成11年度から原研-原電共同研究で基礎データを取得した。 C低減化方法の最適条件を選定するには、対象黒鉛材料の酸化反応と細孔構造に関する基礎データが必要である。ここでは、東海発電所に使用されているペシネQuality1黒鉛及びHTTRで使用されているIG-110黒鉛について、450
C低減化方法の最適条件を選定するには、対象黒鉛材料の酸化反応と細孔構造に関する基礎データが必要である。ここでは、東海発電所に使用されているペシネQuality1黒鉛及びHTTRで使用されているIG-110黒鉛について、450 C
C 800
800 Cの温度範囲における空気酸化特性及び反応の進行に伴う、表面積と細孔分布の変化を調べた。
Cの温度範囲における空気酸化特性及び反応の進行に伴う、表面積と細孔分布の変化を調べた。
西山 勝栄*; 中嶋 悟; 多田 隆治*; 内田 隆*
鉱山地質, 40(5), p.323 - 336, 1990/00
放射性廃棄物の地層処分において、岩盤割れ目からその周辺のマトリックス部への核種の拡散現象は、核種の移動の重要な遅延現象である。そこでこの現象を定量化するため、様々な岩石について、その間隙水中のヨウ素イオンの拡散実験を行い、有効拡散係数を測定した。また、これらの岩石の全間隙率及び間隙孔径分布を測定した。その結果、両対数グラフ上で、岩石の5nm以上の間隙率(transport porosity) traと有効拡散係数は、均質等方的な岩石についてほぼ直線的な関係がある。その傾きから、拡散経路の屈曲度では、
traと有効拡散係数は、均質等方的な岩石についてほぼ直線的な関係がある。その傾きから、拡散経路の屈曲度では、
 =
= tra
tra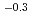 の形でtransport porosityの関数となった。これらの関係は、間隙率を測定し、また間隙率の長期的変化等の推測をすれば、岩盤マトリックス中での核種の拡散現象の定量的予測ができる事を示唆する。
の形でtransport porosityの関数となった。これらの関係は、間隙率を測定し、また間隙率の長期的変化等の推測をすれば、岩盤マトリックス中での核種の拡散現象の定量的予測ができる事を示唆する。
Wang, Q. M.*; Hu, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Zhang, T.*; 深津 勇太; 舘 幸男
no journal, ,
Fluid flow and chemical transport in porous media are the macroscopic consequences of pore structure, which integrates geometry (e.g., pore size and surface area, pore-size distribution) and topology (e.g., pore connectivity). Low-permeability geological media whose pores are poorly interconnected will exhibit the characteristics of anomalous diffusion and sample size-dependent effective porosity, which will strongly impact long-term net diffusion and retention of radionuclides in geological repository settings. A suite of experimental approaches is utilized to study the microscopic pore structure and macroscopic fluid flow and chemical transport for a range of natural rocks (such as clay/shale, crystalline rock, salt), in addition to clay minerals. With a particular focus on quantifying the presence and magnitude of isolated pores for a reduced effective porosity in low-permeability geomedia, the integrated methodologies for basic properties and pore structure characterization include X-ray diffraction, thin section petrography, grain size distribution, water immersion porosimetry, mercury intrusion porosimetry, nitrogen physisorption, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray computed tomography, and (ultra-)small angle neutron (or X-ray) scattering. In addition, custom-designed gas diffusion, tracer recipe involving a range of anionic and cationic chemicals with subsequent analyses by laser ablation and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, along with batch sorption, column transport, and imbibition tests were conducted for coupled effects of pore structure and chemical retention/transport.